Summary
- PCI stands for “Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard“, a mandatory security framework for organizations handling credit card data
- Call centers are high-risk environments due to agents handling sensitive data verbally and the challenge of securing call recordings
- Non-compliance is expensive: Average breach cost is $4.5M+, and fines can reach $100,000+ per month
- 60% of organizations fail their initial PCI audit, indicating widespread compliance gaps
- 10 essential best practices: Redact recordings, secure networks, implement RBAC, use encryption/tokenization, enforce MFA, train staff, and maintain ongoing monitoring
- Your compliance tier determines audit requirements (Level 1-4 based on annual transaction volume)
- PCI DSS v4.0 is now mandatory with stricter requirements for MFA, encryption, and continuous monitoring
- Automated compliance tools can significantly reduce the burden of maintaining PCI compliance
PCI stands for Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard (PCI DSS), a critical security framework that every call center handling payment card information must understand and implement. If your contact center processes, stores, or transmits credit card data, PCI compliance isn’t optional; it’s a legal requirement that protects your customers, your reputation, and your business.
In 2026, data breaches are more costly than ever. The average cost of a single breach now exceeds $4.5 million, and call centers remain prime targets for cybercriminals. Yet approximately 60% of organizations fail their initial PCI compliance audit, indicating widespread gaps in implementation.
This comprehensive guide will walk you through everything you need to know about PCI compliance in call centers, from the fundamentals to actionable best practices that will help you protect cardholder data and avoid costly penalties.
What you’ll learn:
- What does PCI stand for?
- Why PCI Compliance Matters for Call Centers: 2025/2026 Statistics
- The 6 core goals of PCI compliance
- PCI Compliance Tiers: Where Does Your Call Center Stand?
- Top 10 PCI compliance best practices for call centers
- Common PCI Compliance Pitfalls in Contact Centers
- PCI Compliance Checklist for Call Centers
Written by Tushar Jain, CEO of Enthu.AI, with 15+ years of experience in contact center compliance and security.
What does PCI stand for?
PCI stands for “Payment Card Industry.” When combined with DSS (Data Security Standard), it becomes PCI DSS – the Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard.
The full definition
PCI DSS is a comprehensive security framework created in 2006 by the five major payment card brands:
- Visa
- Mastercard
- American Express
- Discover
- JCB
Why it exists
PCI DSS was established to protect cardholder data globally and reduce payment card fraud and data breaches. It sets mandatory security standards for any organization that handles, processes, stores, or transmits credit card information.
Who It Applies To
PCI compliance applies to any call center that:
- Accepts credit card payments over the phone
- Stores cardholder data (even temporarily)
- Transmits payment information through systems
- Has access to customer payment card details
Why call centers are targeted
Call centers are high-risk environments for PCI violations because:
- Agents handle sensitive data verbally – making call recording a compliance challenge
- Multiple touchpoints – data passes through phones, systems, and agent desktops
- Human error – agents may write down card numbers or share data insecurely
- Legacy systems – many call centers use outdated technology that lacks encryption
- High staff turnover – frequent training gaps and inconsistent compliance
Why PCI compliance matters for call centers: 2025/2026 statistics
The stakes for PCI non-compliance have never been higher. Here’s what the data shows:
Payment card fraud & breach statistics
| Metric | 2023 | 2025/2026 | Impact |
| Global payment card fraud losses | $38.5B | ~$42-45B | Increasing annually |
| Average cost per data breach | $3.8M | $4.5M+ | Up 18% year-over-year |
| Organizations failing initial PCI audit | ~55% | ~60% | Majority unprepared |
| Call recording violations | Top 5 violations | Top 3 violations | Most common PCI failure |
| MFA adoption in call centers | ~25% | ~40% | Still lagging the industry |
| Data breaches involving contact centers | 12% of all breaches | 15-18% | Growing target |
Regulatory penalties for non-compliance
Non-compliance with PCI DSS can result in:
- Fines: $5,000 to $100,000+ per month from card brands
- Breach notification costs: $50-$300 per affected customer
- Reputational damage: Loss of customer trust and business
- Legal liability: Lawsuits from affected customers
- Operational disruption: System shutdowns and mandatory remediation
The 6 core goals of PCI compliance
PCI DSS is organized around six core goals designed to protect cardholder data:
Goal 1: Establish and implement strong access control measures
- Implement role-based access controls (RBAC)
- Restrict agent access to only the necessary cardholder data
- Use unique user IDs and strong passwords
- Enforce Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA)
Goal 2: Protect cardholder data
- Encrypt data in transit and at rest
- Implement tokenization for payment processing
- Mask sensitive data in call recordings
- Use secure payment channels (e.g., IVR for card entry)
Goal 3: Maintain a vulnerability management program
- Keep systems patched and updated
- Run regular vulnerability scans
- Use antivirus and anti-malware tools
- Conduct annual penetration testing
Goal 4: Implement strong access control measures
- Monitor and restrict physical access to cardholder data
- Implement network segmentation
- Use firewalls and intrusion detection systems
- Log and monitor all access to cardholder data
Goal 5: Regularly monitor and test networks
- Conduct quarterly vulnerability assessments
- Perform annual penetration testing
- Monitor network activity in real-time
- Track and log all access to cardholder data
Goal 6: Maintain an information security policy
- Document all security policies and procedures
- Train all staff on PCI compliance
- Conduct regular security awareness training
- Maintain audit trails and compliance documentation
PCI compliance tiers: Where does your call center stand?
Your PCI compliance requirements depend on your transaction volume. The PCI SSC defines four compliance levels:
| Tier | Annual Card Transactions | Requirements | Audit Frequency |
| Level 1 | >6 million | Full PCI DSS compliance + annual audit by Qualified Security Assessor (QSA) | Annual |
| Level 2 | 1-6 million | Full PCI DSS compliance + annual self-assessment questionnaire (SAQ) | Annual |
| Level 3 | 20,000-1 million | Full PCI DSS compliance + annual SAQ | Annual |
| Level 4 | <20,000 | Full PCI DSS compliance + annual SAQ or attestation | Annual |
Note: Even Level 4 organizations must maintain full PCI DSS compliance. The tier only affects audit requirements, not compliance obligations.
Top 10 PCI compliance best practices for call centers
Handling payment data comes with serious responsibility. A single slip-up can lead to a costly data breach or compliance violation. That’s why PCI compliance isn’t just a checklist, it’s a mindset. Here are 10 practical strategies to help your call center stay compliant, protect customer data, and avoid penalties.
1. Redact sensitive information from call recordings
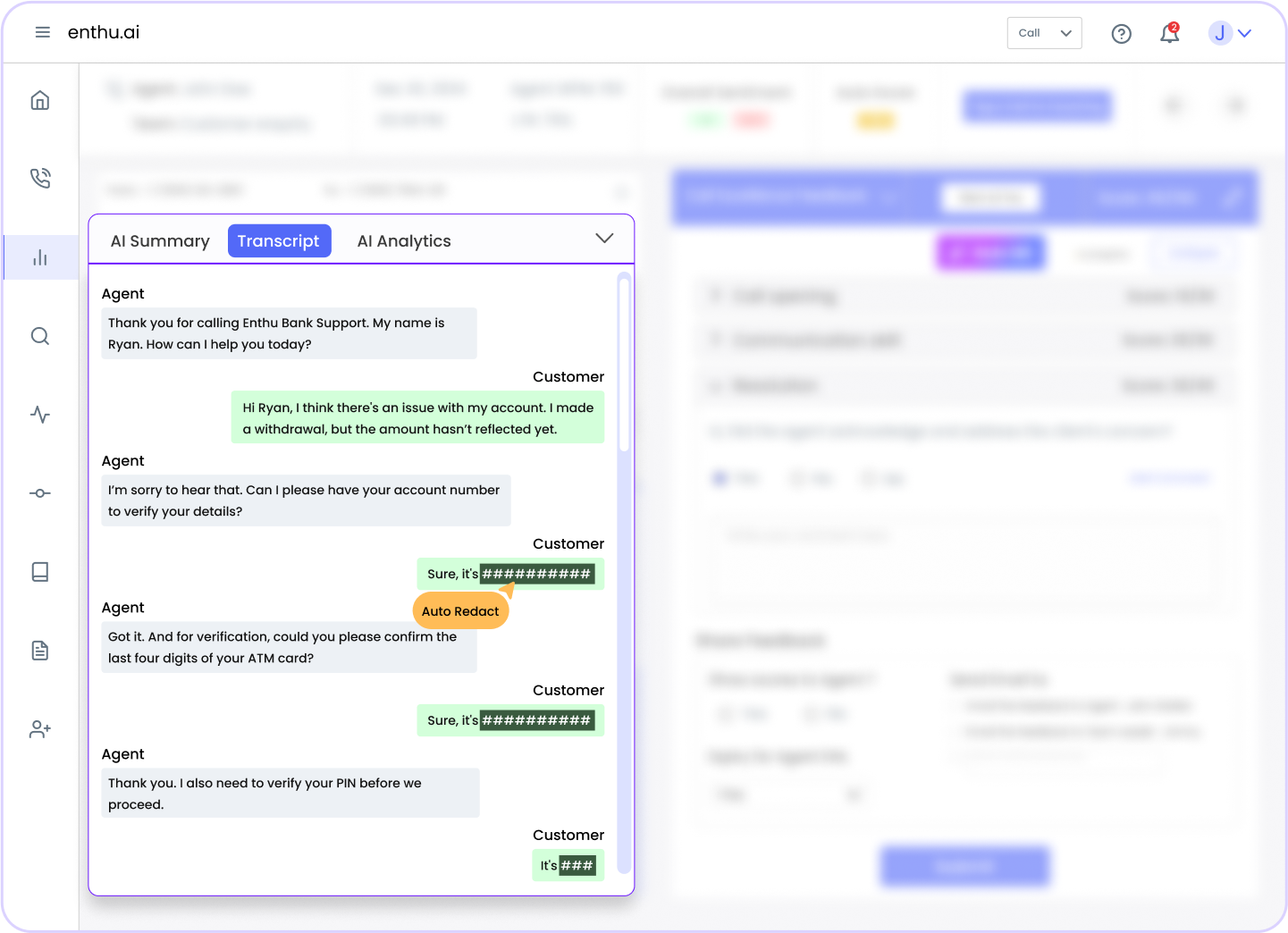
When customers share their credit card details on a call, that information can accidentally get recorded.
Things like the 16-digit card number, CVV, or expiration date should never be stored, even in voice recordings.
Call recordings are often stored for training, audits, or dispute resolution.
But if they include sensitive payment data, they become a goldmine for hackers.
A single breach can expose hundreds or even thousands of card numbers, leading to fraud, fines, and loss of trust.
How to fix this?
Use tools that automatically pause or mute the recording when payment information is entered.
Some systems even detect sensitive data patterns (like 16-digit numbers) and remove them from recordings.
If agents manually key in data, make sure screen recording is paused during entry.
Tools: Enthu.AI’s Conversation Intelligence platform includes automated redaction capabilities.
2. Secure your network and infrastructure
Your call center’s network is like a door to all your systems. If that door is unlocked, hackers can easily walk in and steal sensitive payment data. That’s why securing your network is a big part of PCI compliance.
What does this mean?
You need to protect everything, your internet connection, internal systems, and even the phones your agents use. A weak firewall or open port can be all it takes for cybercriminals to get in.
What can you do?
- Set up firewalls to block unauthorized access.
- Use secure Wi-Fi networks and turn off guest access.
- Regularly check your systems for vulnerabilities with network scans.
- Install intrusion detection systems to catch anything suspicious.
3. Implement role-based access controls
Not everyone in your call center needs access to all payment data. Giving full access to every employee can increase the risk of data leaks or breaches.
What does this mean?
Role-based access control (RBAC) means setting permissions based on a person’s job role. For example, a supervisor might access more data than a regular agent. This limits who can see or handle sensitive cardholder information.
How to do it?
- Define clear roles for all employees.
- Assign access only to systems and data necessary for their job.
- Regularly review and update these permissions.
- Remove access immediately when someone leaves the company or changes roles.
4. Restrict agent use of pen, paper & mobile devices
Using pen and paper or personal mobile devices during calls can lead to accidental leaks of sensitive card data. When agents write down card numbers or store them on phones, it increases the risk of theft or loss.
Why is this risky?
Physical notes can be misplaced or seen by unauthorized people. Mobile devices might not have proper security, making stored information vulnerable to hacking or sharing.
How to prevent this?
- Ban writing down card details on paper during calls.
- Prohibit using personal phones or devices to capture or store payment information.
- Use secure, PCI-compliant tools and software that mask or tokenize card data on screen.
- Train agents on the risks of recording sensitive data outside secure systems.
5. Use strong encryption and key management
Encryption protects cardholder data by turning it into unreadable code during storage and transmission. Strong encryption makes it very hard for hackers to steal or misuse sensitive data.
Why is this important?
Without encryption, data can be intercepted and read easily when sent over networks or stored in databases.
How to do it right?
- Use industry-standard encryption methods like AES-256.
- Encrypt all cardholder data both when it’s stored and when it’s sent across networks.
- Manage encryption keys securely, store keys separately and rotate them regularly.
- Limit access to keys only to authorized personnel.
6. Adopt tokenization and secure payment channels
Tokenization replaces sensitive card data with a random string of characters called a token. This token has no value outside your system, so even if intercepted, it’s useless to attackers.
Why use tokenization?
It reduces the amount of sensitive data your call center stores, lowering risk. If tokens are stolen, the real card data remains safe.
Secure payment channels mean using safe methods for customers to provide payment info, like secure web forms or encrypted phone systems. This helps protect data during transmission.
7. Regularly update antivirus and anti-malware tools
Antivirus and anti-malware software protect your call center from harmful viruses and attacks.
These threats can steal or damage sensitive cardholder data. Outdated software may not catch new viruses.
What does this mean?
It means your call center must keep all antivirus and anti-malware software up to date.
Old or outdated software cannot protect against the latest threats, leaving your network vulnerable to attacks that can steal cardholder data.
How to do it?
- Set your antivirus tools to update automatically.
- Schedule regular scans on all computers and devices.
- Ensure every device on your network has active and updated antivirus software.
- Train your IT team to monitor updates and respond to alerts quickly.
- Regular updates help prevent malware infections and protect customer data.
8. Enforce Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA)
Passwords alone aren’t enough to protect sensitive data. Hackers can steal or guess passwords easily. Multi-factor authentication (MFA) adds a second step to verify a user’s identity.
What does it mean?
MFA means users must provide two or more forms of verification before accessing systems. This could be a password plus a text message code, an app-generated code, or biometric info like a fingerprint. Even if a password is stolen, MFA stops unauthorized access.
How to do it?
- Require MFA for all employees handling payment info or sensitive data.
- Use authentication apps (Google Authenticator, Microsoft Authenticator) or hardware tokens.
- Enable MFA on VPNs, email, CRM, and call center software.
- Train agents on why MFA matters and how to use it.
- Regularly review MFA settings and update as needed.
9. Treat PCI Compliance as an Ongoing Process
PCI compliance isn’t a one-time task. It’s a continuous effort to keep your call center secure. Threats change. Technology evolves. So should your compliance practices.
What does it mean?
It means regularly reviewing and updating your security policies, tools, and procedures to meet PCI standards. You don’t “achieve” compliance once and forget about it. Instead, you build a system that keeps evolving to stay secure and compliant.
How to do it?
- Schedule regular PCI compliance audits and gap assessments
- Update policies and procedures as per the latest PCI DSS changes
- Set quarterly reviews to evaluate tools, processes, and team readiness
- Keep all departments informed of compliance requirements and updates
- Work with IT and compliance teams to ensure ongoing improvements
- Stay up-to-date with new threats and evolving best practices
10. Train Agents and Reinforce Compliance Behavior
Your agents are the front line of your call center. Even with strong systems in place, a single mistake by an agent can lead to a data breach.
What does it mean?
It means giving agents the right knowledge and tools to handle sensitive data. They should understand what PCI compliance is, why it matters, and how their actions impact it. Training shouldn’t be a one-time session; it must be ongoing, relevant, and practical.
How to do it?
- Conduct regular PCI compliance training during onboarding and at intervals
- Use real-world scenarios to teach how to handle sensitive payment data
- Share updates when PCI DSS standards change
- Set up monthly quizzes or mini refresher sessions
- Encourage managers to lead by example in enforcing compliance
- Recognize and reward compliant behavior to reinforce good practices
- Use Call Center Quality Monitoring Software to audit compliance during calls.
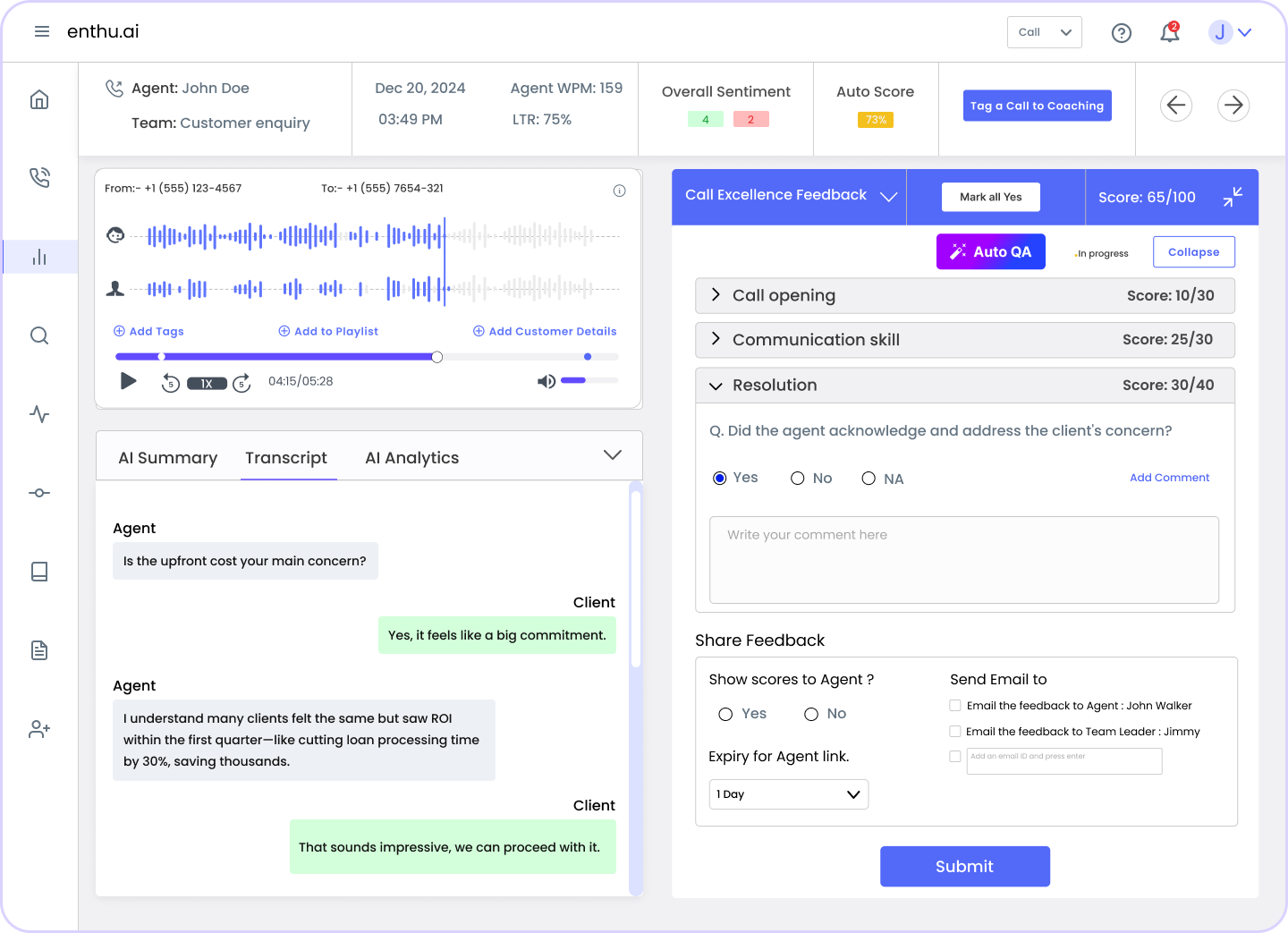
Common PCI Compliance Pitfalls in Contact Centers
Even with best practices in place, many call centers struggle to stay fully PCI compliant. Small oversights can lead to major data breaches and fines.
Let’s look at two of the most common pitfalls that weaken compliance efforts.
Pitfall 1: Inconsistent enforcement
Policies exist, but they aren’t applied the same way across teams, locations, or shifts. What one agent gets away with, another might be penalized for.
Compliance isn’t optional. One weak link can expose customer data, and your business, to risk. Regulators won’t consider internal inconsistency a valid defense.
What you can do:
- Standardize policies across all teams and vendors.
- Use QA software to track adherence.
- Conduct surprise audits to catch gaps.
- Appoint PCI champions per team to ensure accountability.
- Reinforce policies during team huddles or weekly reviews.
Pitfall 2: Poor training & outdated infrastructure
Your agents may not understand what PCI compliance even means. And your systems?
They might be running on outdated frameworks that don’t support modern security protocols.
Untrained agents + old tech = a data breach waiting to happen. Even a small error (like saving a card number in notes) could lead to hefty fines.
What you can do:
- Offer regular PCI refresher training sessions.
- Upgrade outdated systems with PCI-compliant tools.
- Simulate real-world compliance scenarios during training.
- Include compliance metrics in agent performance reviews.
- Partner with IT to stay ahead of security updates.
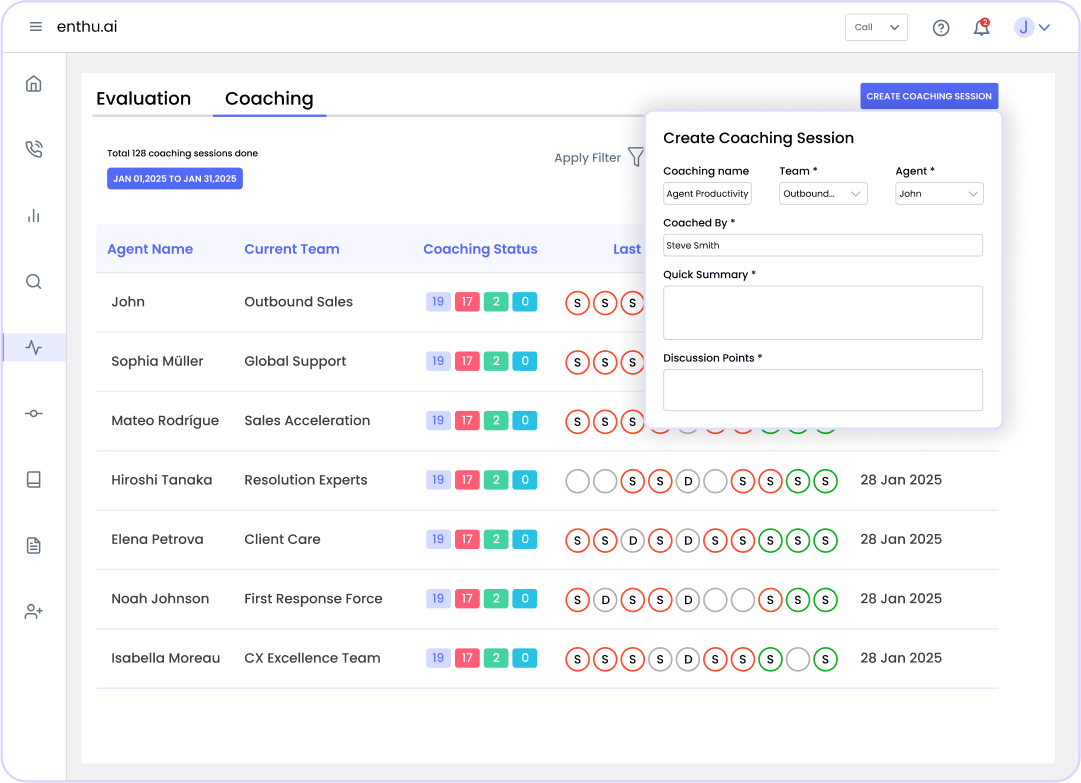
PCI compliance checklist for call Centers
Use this checklist to assess your current compliance status and identify gaps:
Network security
- Firewalls are deployed and properly configured
- The network is segmented to isolate cardholder data
- Intrusion detection/prevention systems are in place
- Quarterly vulnerability scans are conducted
- Annual penetration testing is performed
Access control
- Role-based access controls (RBAC) are implemented
- Unique user IDs are assigned to all users
- Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA) is enforced for admin access
- Access is reviewed and updated quarterly
- Unused accounts are disabled within 90 days
Data protection
- All cardholder data is encrypted in transit (TLS 1.2+)
- All cardholder data is encrypted at rest (AES-256+)
- Tokenization is used for payment processing
- Call recordings are automatically redacted
- Full card numbers are never stored
Vulnerability management
- Antivirus/anti-malware is deployed on all systems
- Systems are patched within 30 days of release
- Vulnerability scans are conducted quarterly
- Penetration testing is conducted annually
- Security updates are tracked and documented
Monitoring and logging
- All access to cardholder data is logged
- Logs are retained for at least 1 year
- Log reviews are conducted monthly
- Suspicious activity is investigated immediately
- Audit trails are protected from tampering
Training and awareness
- All staff receive PCI training during onboarding
- Quarterly refresher training is conducted
- Training completion is documented
- Agents are tested on PCI knowledge
- Compliance is reinforced through policies
Policies and documentation
- PCI compliance policy is documented and approved
- Security policies cover all 12 PCI DSS requirements
- The incident response plan is documented
- Data retention policy is defined
- Policies are reviewed and updated annually
Compliance assessment
- The compliance tier is identified based on transaction volume
- The annual self-assessment questionnaire (SAQ) is completed
- Qualified Security Assessor (QSA) audit is scheduled (if required)
- Compliance gaps are documented
- The remediation plan is in place
Conclusion
PCI compliance isn’t just about passing audits or avoiding fines. It’s about building customer trust, every single day. In call centers, where agents handle sensitive data around the clock, even one slip can break that trust permanently.
What sets secure, high-performing centers apart isn’t just technology. It’s discipline, training, and a culture of accountability.
Don’t wait for a breach to tighten your systems. Don’t treat PCI as a once-a-year headache. Instead, embed it into your daily workflows. Empower your agents. Equip your systems. And lead with the mindset that compliance is a business advantage, not a burden.
The cost of being proactive? Some planning and process. The cost of neglect? Your reputation. Your call.
FAQs
1. What does PCI stand for in BPO?
In BPO (Business Process Outsourcing), PCI stands for Payment Card Industry. It refers to the set of standards and regulations designed to protect sensitive payment card information handled by outsourced service providers.
2. What is the PCI compliance process?
The PCI compliance process involves assessing your current data security measures, implementing necessary safeguards according to PCI DSS (Data Security Standard) requirements, conducting regular audits and vulnerability scans, and maintaining ongoing adherence to these standards to ensure the protection of cardholder information.
3. What does PCI stand for in customer service?
In customer service, PCI stands for Payment Card Industry. It encompasses the guidelines and standards set to ensure that customers’ payment information is securely handled and protected during service interactions.




 On this page
On this page